State of the art
As you can see the historical development, required the world's wind energy technician 5000 years to reach a power per m2 swept rotor area of 400 to 450 watts for the three-leaf plants (1,000 kW up at rated wind speed of 12 m / sec). The three-leaf plants up to 50 kW power is currently at a maximum of 350 W/m2.
The revolutionary Windgiant wind turbine system opened up new physical performance limits in a relatively short development time, and reached for a 20 kW and 30 kW system, more than 2000 watts per m2 at a rated wind speed of 12 m / sec.
Stages of development of wind energy 3000 BC to 21 Century
Persian grain mill: 3000 to 700 years before Christ
The oldest was the use of wind power in Persia it
With the wind, the grain mills were powered. The turbines were running horizontal wooden wheels strung with linen cloths.
Existing remains of the wall are now listed.
Power per m2 swept area: No data available


Greek and Spanish windmills: 11-17 century (1000 to 1700 N. Christ)
Were used as grain mills and transport for water in agriculture.
Standing in many countries listed.
Power per m2 swept area: 25 to 100 watts


Dutch windmills: 18th century (1701 to 1800)
This historic windmills in Holland in the 18th century brought a grain mills.
Are now largely a historical monument
Power per m2 swept area: 80 to 120 watts


American Windmills: 19th century (1801 to 1900)
This historic windmill was used in America and Australia for drinking water and Tränkwassergewinnung for agriculture.
Power per m2 swept area: 100 to 150 watts

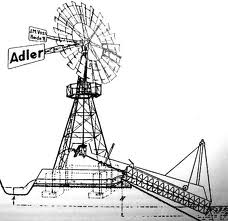

Around 1880 in Europe about 200,000 windmills were in use.
Three-wing wind turbines: 20th century (1930 to present)
The mid-70s was the three-leaf plant by wind power worldwide, with this system
finds the most part in large-scale wind farms.
Efficient performance per m2 of rotor area by the wing geometry, only more limited.
(max. possible to 10%)
Power per m2 swept area: 280 to 450 watts

Shaped turbine wind turbines: 21 Century (2001 to present)
The previous use of wind energy is pushed at the maximum power output per m2 swept to its limits. Efficient performance increases per m2 of painted surface are possible at the present state of the art only through innovative technologies such as the turbine-shaped wind turbines by using the WAVE system.
Power per m2 overlined turbine / rotor area: 1250 to 2000 Watts













